Following points are used
1. Check whether the last digit of the integer can be divided by 2 or not
2. Check whether the sum of all digits of the integer can be divided by 3 or not
3. Check whether the last digit of the integer can be divided by 5 or not
4. If all the above checks fails Check whether there is an integer from 7 to square root of number which is divide the number
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
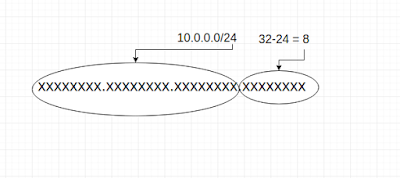
How to choose IP address range for resources for AWS virtual private cloud
You will often need to allocate an IP address range when you design the network of an AWS VPC. Since VPC is a small network of resources(E...
-
You can create OAuth applications using OAuthAdminService admin service. You can follow the below steps to see how mapping of existing OAu...
-
You will often need to allocate an IP address range when you design the network of an AWS VPC. Since VPC is a small network of resources(E...
-
What is Apache FOP? Apache FOP is a print formatter driven by XSL formatting objects(XSL-FO). It is a library to read XSL FO objects and ge...



No comments:
Post a Comment